Exploring the world of Best Antidepressant Discussions in Clinical Settings, this introduction aims to provide a deep dive into the intricacies of antidepressant treatments in clinical settings. From the various types of antidepressants to personalized treatment approaches, this topic delves into the nuanced decisions made in selecting the most effective antidepressant for each individual.
This engaging discussion will shed light on the complexities of antidepressant choices and the considerations that clinicians take into account when determining the best course of treatment for their patients.
Types of Antidepressants
Antidepressants are a common treatment for depression and other mood disorders. There are several classes of antidepressants commonly used in clinical settings, each with its own mechanism of action and potential side effects.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
SSRIs are one of the most commonly prescribed classes of antidepressants. They work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, which helps regulate mood. Examples of SSRIs include:
- Prozac (fluoxetine)
- Zoloft (sertraline)
- Lexapro (escitalopram)
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
SNRIs are another class of antidepressants that work by increasing levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain. This dual action can be beneficial for individuals who do not respond to SSRIs alone. Examples of SNRIs include:
- Cymbalta (duloxetine)
- Effexor (venlafaxine)
- Pristiq (desvenlafaxine)
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
TCAs are an older class of antidepressants that are not as commonly prescribed today due to their side effect profile. They work by blocking the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. Examples of TCAs include:
- Amitriptyline (Elavil)
- Imipramine (Tofranil)
- Nortriptyline (Pamelor)
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
MAOIs are another older class of antidepressants that are reserved for individuals who do not respond to other treatments due to their potential interactions with certain foods and medications. They work by inhibiting the enzyme monoamine oxidase, which breaks down neurotransmitters like serotonin.
Examples of MAOIs include:
- Nardil (phenelzine)
- Parnate (tranylcypromine)
Efficacy and Side Effects
Antidepressants are commonly used in clinical settings to help manage various types of depression. Understanding the efficacy rates and potential side effects of different antidepressants is crucial in selecting the most suitable treatment for each patient.
Efficacy Rates of Antidepressants
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) are often considered first-line treatment due to their effectiveness in treating major depressive disorder.
- Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) have shown efficacy in treating certain types of depression, but they are associated with more side effects compared to newer antidepressant classes.
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) are usually reserved for patients who do not respond to other antidepressants, as they have shown efficacy in treatment-resistant depression.
Common Side Effects Associated with Antidepressants
- SSRIs may cause side effects such as nausea, insomnia, and sexual dysfunction.
- TCAs are known for side effects like dry mouth, constipation, and dizziness due to their anticholinergic properties.
- MAOIs can interact with certain foods and medications, leading to potentially dangerous side effects like hypertensive crisis.
Balance between Efficacy and Side Effects
Antidepressant selection involves considering the balance between efficacy and side effects to optimize treatment outcomes for each patient. Healthcare providers must weigh the potential benefits of a specific antidepressant in alleviating depressive symptoms against the risk of adverse effects. Individual patient factors, such as comorbidities and medication tolerability, play a crucial role in determining the most appropriate antidepressant therapy.
Individualized Treatment Approaches
Personalized medicine plays a crucial role in selecting the most appropriate antidepressant for a patient, taking into account various factors that can influence treatment outcomes. Factors such as age, comorbidities, and previous treatment responses are key considerations in tailoring antidepressant therapy to meet the individual needs of each patient
Age
Age is an important factor to consider when choosing an antidepressant for a patient. For example, older adults may be more sensitive to certain side effects of antidepressants, such as dizziness or drowsiness. Therefore, selecting an antidepressant with a favorable side effect profile becomes essential in this population.
Comorbidities
Patients with comorbid conditions, such as anxiety disorders, substance abuse, or chronic pain, may require antidepressants that can effectively target both their depression and coexisting conditions. For instance, selecting an antidepressant with anxiolytic properties may be beneficial for a patient with depression and anxiety disorders.
Previous Treatment Responses
Understanding a patient's history of antidepressant treatment is crucial in determining the most suitable option for ongoing therapy. If a patient has previously shown poor response or intolerable side effects to a specific class of antidepressants, an alternative class or a different medication within the same class may be considered to optimize treatment outcomes.
Emerging Trends and Research
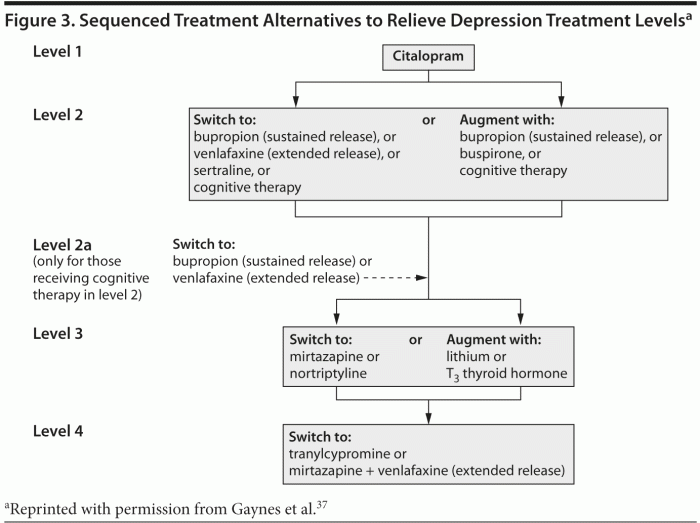
Antidepressant research is constantly evolving, with new treatments and mechanisms of action being explored to improve outcomes for individuals struggling with depression. Let's delve into some of the latest trends and findings in the field.
New Antidepressant Treatments
In recent years, there has been a surge in the development of novel antidepressants that target different pathways in the brain. For example, ketamine, originally used as an anesthetic, has shown promising results in treating treatment-resistant depression. Its rapid-acting effects have sparked interest in its potential as a breakthrough treatment option.
Additionally, researchers are investigating the use of psychedelics like psilocybin for their antidepressant properties, opening up a new frontier in mental health treatment.
Novel Mechanisms of Action
Researchers are exploring innovative mechanisms of action for antidepressants to enhance efficacy and reduce side effects. One area of interest is the gut-brain axis, with studies suggesting a link between gut health and mental well-being. Probiotics and psychobiotics are being studied for their potential role in modulating mood and alleviating depressive symptoms.
Furthermore, advancements in personalized medicine are paving the way for tailored treatment approaches based on an individual's unique biology and genetic makeup.
Treatment-Resistant Depression
The challenge of treatment-resistant depression has led to a shift in focus towards identifying alternative treatment options. Research findings on the efficacy of interventions such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) in resistant cases have sparked discussions on the best course of action for individuals who do not respond to traditional antidepressants.
The emergence of new therapies and treatment modalities offers hope for those who have not found relief with conventional medications.
Closing Notes

In conclusion, the discussion on Best Antidepressant Discussions in Clinical Settings reveals the importance of personalized medicine and ongoing research in shaping the landscape of antidepressant treatments. By understanding the nuances of different antidepressant classes and considering individual patient characteristics, clinicians can optimize treatment outcomes and improve the quality of care provided to those suffering from depression.
Essential FAQs
How do SSRIs differ from TCAs in their mechanisms of action?
SSRIs primarily work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, while TCAs inhibit the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine, leading to different side effect profiles.
What factors are considered when selecting the best antidepressant for a patient?
Factors such as the patient's age, comorbidities, previous treatment responses, and potential side effects are all taken into account when choosing the most suitable antidepressant.
Are there any new antidepressant treatments on the horizon?
Research is ongoing on novel antidepressants with different mechanisms of action, offering hope for more effective treatments in the future.